Why Youth Mentors Must Understand the Implications of Generational Succession
In a new twist christened the GenZ revolution, the unfolding youth-driven agitation for change in Kenya cannot be let go without the voice of reason founded on a base of knowledge and research. Impact Borderless Digital (IBD), a youth mentorship platform founded in 2019 after years of engaging the youth in knowledge and technology-led conversations and skills development, can now share a timely excerpt on generational succession, taken off the pages of the seasoned IBD mentorship manual.
The views shared here resonate with an earlier exposition by the IBD Founder, which isolated technology as a potent quadrant of geopolitical influence, unique as a pillar that can power innovation without diminishing returns.
The Intergenerational Mentorship Challenge
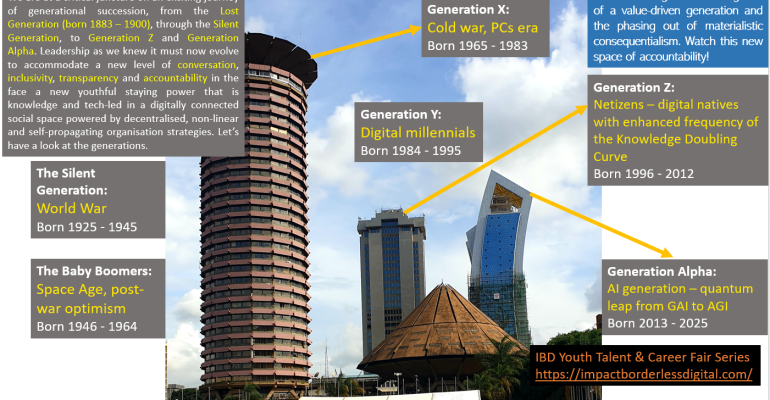
“The birth of a value-driven generation and the phasing out of materialistic consequentialism” is the central theme of the message today. It suggests a shift in societal values from materialism to more value-driven principles. This youth mentorship platform, under the Impact Borderless Digital (IBD) Youth Talent and Career Fair Series, has been consistent in messaging the implications of generational succession, underscoring that youth mentors must understand this succession in depth because the generational gap keeps widening as they mentor younger and younger people over the years. A graphic illustration of the generations as we know them by their birth years communicates the associated changes in worldviews.
New Against Old Methods
The current protests being witnessed in Kenya against the Finance Bill 2024 are a case in point. The surprisingly youth-driven and non-violent protests have taken on a new trajectory driven by GenZs deploying new, decentralised, non-linear and socially connected online and pervasive methods, all fuelled by a fearless, issue-based and self-propagating resolve that totally confounds the tactics and convictions of the older generations, who are still practising antiquated, linear, centralised, and limited hard-path approaches. Suppose this new generation of protests could continue to embrace brainpower over brawn, intellect powered by information and passion as opposed to brute force oiled centrally using money from sponsors. In that case, the new way remains commendable, and the police should reciprocate with a non-violent response.
Towards Value-Driven Resolve and Pursuits
Materialistic consequentialism, as referred to here, is a belief that the end in terms of material and wealth accumulation justifies the means irrespective of the impurity of the process. Fortunes have been lost to corruption through such unjust pathways to selfish ends. If GenZs as representatives of a new worldview driven by values can save this worsening crisis in society, then their leaders and seniors must wake up to the dawn of a new world. The following key aspects and characteristics are important guides for the emerging reality and new leadership challenges in a world welcoming adult GenZs and their successors.
Birth of a Value-Driven Generation
Definition and Characteristics:
Value-Driven: Prioritising intrinsic values such as honesty, empathy, sustainability, and community over material wealth and possessions.
Characteristics: Ethical consumerism, emphasis on social justice, environmental consciousness, focus on mental well-being, and community-oriented behaviours.
Causes and Influences:
Education: Increased awareness through education systems emphasising moral and ethical values.
Technology and Information: Easy access to information highlighting global issues, fostering empathy and global awareness.
Economic Factors: Economic instability makes material wealth less reliable and valued.
Cultural Shifts: Influences from cultural icons, media, and movements promoting non-materialistic values.
Manifestations in Society:
Consumer Behaviour: Preference for sustainable and ethical products and sharing economy models.
Work and Career: Choosing careers that align with personal values and offer meaningful contributions.
Social Movements: Participation in movements advocating for social justice, environmental protection, and ethical governance.
Phasing Out of Materialistic Consequentialism
Definition and Characteristics:
Materialistic Consequentialism: Belief that the value of actions is primarily determined by material outcomes and wealth accumulation.
Characteristics: Consumerism, prioritisation of economic growth over social and environmental well-being, individualism, and short-term gains.
Manifestations:
Environmental Concerns: Environmental impact of consumerism leading to unsustainable practices.
Social Inequality: Social disparities caused by unchecked materialism, driving inequalities.
Psychological Factors: Realisation of the limits of material wealth in achieving happiness and fulfilment.
Global Crises: Events such as pandemics, economic recessions, and climate change highlighting the fragility and unsustainability of materialistic lifestyles.
Remedial Measures in Society:
Shift in Values: Greater emphasis on long-term sustainability, ethical behaviour, and community welfare.
Policy and Governance: Implementation of policies promoting sustainability, social equity, and corporate responsibility.
Corporate Practices: Businesses adopting corporate social responsibility/development (CSR) and sustainable practices to align with changing consumer values.
Implications and Future Directions
With sustained momentum and staying power, the new resolve by new generations should lead to aspirational states marked with the following qualities.
Economic Impact:
Market Changes: Growth in markets for ethical and sustainable products.
Business Models: Shift towards circular economy models and sustainable business practices.
Social Impact:
Community Engagement: Increased participation in community-driven initiatives and grassroots movements.
Quality of Life: Potential improvements in overall well-being and mental health as focus shifts from material wealth to value-driven living.
Environmental Impact:
Sustainability: Enhanced efforts towards environmental conservation and sustainable resource use.
Climate Action: Greater public support for policies addressing climate change and environmental degradation.
Way Forward for New Outcomes
The transition from materialistic consequentialism to a value-driven generation signifies a profound shift in societal values. This change is driven by a combination of economic, environmental, and social factors, leading to a more sustainable, equitable, and fulfilling way of life. The future likely holds a sustained emphasis on values over material wealth, reshaping various aspects of society including consumer behaviour, corporate practices, and policy-making. Technology, now the fourth quadrant joining the traditional pillars of geopolitical influence that have been known to be economic strength, trade, and military power, grants digital natives — Gen Z and their successors — unprecedented access to boundless possibilities and distant horizons. As a key implication, any youth mentor or leader, to be taken seriously in the new era, must understand the generational succession wave and resonate with it in their methods, decisions, and interventions.
By Dr Nashon Adero
#IBD Series
This is the product of more than a decade of dedicated experience in research, skills development, training, and mentorship. Through mentorship and career development fora, IBD empowers youth with the knowledge, international exposure, and digital fluency they need to be emancipated global citizens with borderless influence for sustainable development.
