Franchising: Key to SME Development
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) play an important role in absorbing manpower, especially in developing countries like Indonesia, reducing poverty and consequently spurring economic growth. Since SMEs do not make use of sophisticated technology, they are able to engage people with low education who would otherwise not be absorbed by major companies.
Pressure from competition has triggered SMEs to be more creative, accumulate knowledge and develop their manpower. As SMEs do not concentrate in one location as big factories do, they spread income thereby decreasing economic disparities between big cities and suburbs. Big companies or MNCs can only absorb manpower with certain competence usually unaffordable by the people at the bottom of the pyramid. MNCs also restricted in terms of location unlike SMEs which are flexible and have a wider coverage. The SME capability is however limited by insufficient capital and low employee improvement.
Two-thirds of the world population lives under the minimum standard of life (US$1,500/annum according to UN). Most of them earn below USD1 a day through informal economic activities. In developing countries, 40 per cent to 60 per cent of the economic activities are informal sector driven and are claimed to be at the bottom of the pyramid. Improving this 40 per cent to 60 per cent portion of economic activities will boost the economic growth. Increase in the population’s purchasing power means improvement of its potential market and opening bigger opportunities to the business world.
Franchise Business and SME Improvement
Franchising holds an important role in the improvement of SMEs in a country. It is a form of collaboration between a big company (the franchisor), with a SME as the legal holder of franchise management by using the franchisor’s brand. A Franchise business facilitates newcomers in the business world through its package of tested business and management concepts as well as its operating procedures.
Franchising has its own uniqueness known as Business Format Franchising (BFF), the comprehensive operational activity framework that must be implemented by the franchisee. BFF is a result of a franchisor’s exploration of various business possibilities, resulting in a formula of combining resources with business processes most suitable to the culture and the brand it has. Using the formula as a working template, the franchise business replicates its outlets through the franchisee. To protect its own image, the franchisor provides training and managerial assistance to the franchisee.
The franchise business is not just an ordinary cooperation between a big corporation and SME, or capital investment for the business development with certain profit share. Franchising involves transfer of asset specificity, tangibles and intangibles. Franchising is a business synergy between a mature company and its superior performance supported by a wide knowledge base, resources and high entrepreneurial orientation, with a small company that most likely lacks competence and experience.
Although franchising imposes certain rules to the SME in its operation, it also allows the franchisee to make certain adaptations to its environment to gain certain market share.A company’s capabilities lie in its knowledge to manage its limited resources. This knowledge is partly accumulated through interaction with individuals and other organizations, consequently increasing its ability to adapt to its environment. Pro-activeness in a company motivates individuals to search for information and possibilities to innovate, in order to gain competitive advantages. Knowledge on market conditions drives the company to anticipate future actins.
Continuous interaction between a company’s environment through its entrepreneurial orientation (pro-activeness, innovativeness, risk taking) and its knowledge based resources through operational/business processes, namely progressive performance, if properly managed will enable a company to gain competitive advantage.
Role of Franchise Business to the Economic Growth
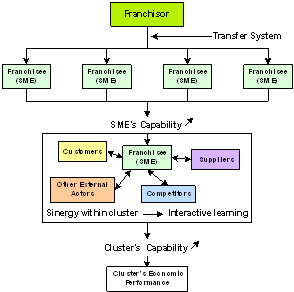
Franchising has an important role in the growth of SMEs and the regional economy as it transfers knowledge to the SME, hence improving employee capability that is usually costly to the SME to fund and making the SME to avoid the trial and error process. Synergy between a franchisee with its supply chain will automatically push the supply chain to match with pre-determined standard and quality. Accordingly, it improves the resource capability in the economic cluster where the SME is operating. The figure below shows the interaction between franchise and its environment.
By Dr. Bambang N. Rachmadi & Marisa D. Pingkan R.
Faculty of Economy
University of
